The Differences Between 5 Different Logistics Providers
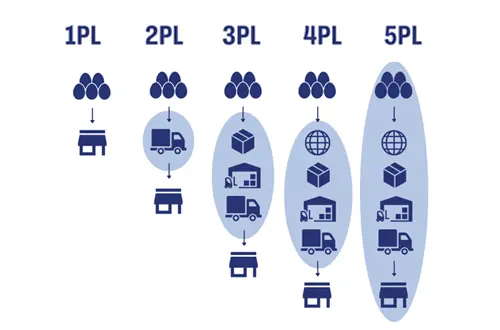
As companies operate globally, there is a need to increase supply chain visibility and reduce risk, increase speed and reduce costs, while requiring a common technology solution. 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL and 5PL refer to different levels of logistics providers in the supply chain industry.
What is the difference between 1pl, 2pl, 3pl, 4pl and 5pl?
1PL (First Party Logistics)
Refers to the logistics and distribution tasks completed by the manufacturer or goods supplier themselves. It is a single service provider specializing in certain goods or transportation methods in a specific geographical area. In this model, the company handles its logistics operations in-house. The organization is responsible for shipping, storing and distributing its own products.
For example: shipping companies, port operators, warehouse companies. The advantage is that the manufacturer's profits flow within the company and will not rely on other logistics providers, thereby ensuring the company's overall benefits. A production company's logistics arm can also become a first-party logistics provider if it has its own transportation assets and warehouses.
Second Party Logistics Provider (2PL)
This involves outsourcing logistics activities to a service provider. The company typically hires transportation and warehousing services from outside suppliers but retains control over its own logistics strategy. is a service provider that provides professional logistics services over a larger geographical area than 1PL.
There is usually a framework contract between the 2PL and the customer, which sets out the conditions for most short-term transport tasks. 2PL provides owned and external logistics resources such as trucks, forklifts, warehouses, etc. for transportation, cargo handling or warehouse management activities. Second-party logistics emerged during the rise of globalization and lean management trends when companies began to outsource their logistics activities to focus on their own core company. Examples include courier, courier and parcel services; ocean carriers, freight forwarders and forwarding providers.
2PL is not integrated; compared to 3PL, it is just an outsourced logistics provider without system integration. 2PLs are often on call (such as express parcel services), while 3PLs are almost always informed of upcoming workloads.
As technology advances, the method of informing 3PLs of inbound workloads often falls on API integrations that connect e-commerce stores to fulfillment centers. Another difference between 2PL and 3PL is the specification and customization of services. 2PLs typically offer only standardized services, whereas 3PLs often offer services that are customized and specialized based on customer needs.
3PL (Third Party Logistics)
It is a logistics form in which third-party logistics companies undertake corporate logistics activities. 3PL provides customers with serialized, personalized and information-based logistics agency services that are bound by contracts and based on alliances. 3PL provides its professional logistics services through cooperation with first or second parties. For example, UPS, chinadivision, Amazon logistics, etc.
Companies outsource logistics activities to third-party providers, which include services such as transportation, warehousing, distribution, and sometimes value-added services such as packaging and order fulfillment.
The cost-effectiveness of a third party logistics provider can only be given with long-term stable contracts and profits. In contrast, second-party logistics services cannot be customized, and considering the fierce market fluctuations and fierce competition, the price war is at a low level. There is another difference between a 2PL and a 3PL: the durability of the contract. 3PL contracts are long-term contracts, while 2PL contracts are less permanent, allowing the customer flexibility to respond to market and price changes.
4PL (Fourth Party Logistics)
does not have its own transportation assets or warehouse capacity, and mainly outsources the entire logistics aspect of the enterprise, and can also take advantage of strategic advice in addition to operational support. It has distribution and integration functions in the supply chain and is designed to improve the efficiency of the supply chain. 4pl logistics providers manage and integrate the entire supply chain for their clients, often acting as consultants and coordinators. They can oversee multiple 3PLs and optimize the supply chain for greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
The advantage of 4PL is that it has a comprehensive understanding of the entire logistics market, outsources the logistics aspects of the enterprise, saves time and money, and can take advantage of strategic advice. However, 4PL has less control over the logistics and fulfillment process and is more expensive. The 4PL provider selects the 3pl logistics provider from the market that best suits the logistics problems of its customers. Unlike the configuration function of 4PL in the supply chain, the core competency of 3PL providers is operational logistics.
Fifth-party logistics providers (5PLs)
provide supply chain management and provide system-oriented consulting and supply chain management services to their customers. Advances in technology and related increases in supply chain visibility and inter-company communication have given rise to a relatively new third-party logistics operating model - the "non-asset-based logistics provider".
1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL and 5PL differ in terms of service scope, service providers and service objects, and each level involves a higher degree of external participation and coordination.
what are third party logistics providers?How 3PL works?
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers typically focus on integrated operations of warehousing and transportation services that can be expanded and customized according to customer needs based on market conditions to meet the needs of their products and delivery service requirements. Services include not only logistics but also value-added services related to the production or procurement of goods, such as services that integrate various parts of the supply chain. 3PLs target specific functions within supply management, such as warehousing, transportation, or raw material supply.
Standard 3PL provider
This is the most basic form of a 3PL provider. They will perform activities that are the most basic functions of logistics such as picking and packing, warehousing and distribution (operations). For most of these companies, the 3PL function is not their main activity.
service developer
Such 3PL providers will provide customers with advanced value-added services such as: track and trace, cross-docking, specific packaging or providing unique security systems. A solid IT foundation and a focus on economies of scale and scope will enable such a 3PL provider to perform these types of tasks.
client adapter
This type of 3PL provider emerges at the request of its customers and essentially has complete control over the company’s logistics activities. 3PL providers have greatly improved logistics but have not developed new services. Such 3PL providers typically have a small customer base.
Customer Developer
This is the highest level a 3PL provider can achieve in terms of its processes and activities. This occurs when a 3PL provider integrates itself with a customer and takes over its entire logistics function. These providers have few clients but perform a wide range of detailed tasks for them.
Why choose 3pl?
Choosing a third-party logistics (3PL) provider can offer a variety of advantages to businesses looking to streamline their supply chain and logistics operations. Including but not limited to the following aspects:
Global Reach: For companies involved in international trade, a 3PL typically has a global network of partners, carriers, and warehouses. This can make cross-border logistics smoother and more efficient.
Professional services: 3PL companies focus on logistics and supply chain management, have professional skills and experience, and can provide comprehensive logistics solutions to help companies improve logistics efficiency and reduce costs. They bring industry knowledge, expertise and resources to help businesses benefit from the latest technology, best practices and efficient processes.
Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing logistics to a 3PL provider often results in cost savings. 3PL companies usually have a large number of customers and resources, and are able to reduce costs through large-scale operations and achieve cost efficiencies through shared resources.
Flexible customization: 3PL companies can provide customized services according to the needs of enterprises, and also allow enterprises to adjust logistics services according to fluctuations in demand. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for companies that experience seasonal changes in their operations. Help enterprises respond to different business needs and market changes.
Technology Integration: Many 3PLs invest in advanced technology, such as chinadivision’s warehouse management system (WMS), transportation management system (TMS), and tracking tools. This integration can improve supply chain visibility, accuracy, and overall efficiency.
Reduce enterprise burden: Enterprises can outsource logistics and supply chain management to 3PL companies, thereby reducing their own operational and management burden without investing in their own warehouses, transportation fleets and other infrastructure. This allows for significant upfront cost savings and allows you to focus on growing your core business.
Improved customer service: A reliable 3PL can improve customer service by providing faster, more accurate order fulfillment, better inventory management, and enhanced overall supply chain visibility.
Improve efficiency: Through advanced logistics technology and operating models, 3PL companies can improve the logistics efficiency and supply chain management level of enterprises, and reduce inventory and transportation costs.
Risk Management: 3PL providers can help manage and mitigate risks in the supply chain. This includes handling regulatory compliance, implementing security measures, and developing contingency plans for unexpected disruptions.
Choosing 3PL can bring professional, efficient, flexible and low-cost logistics services to enterprises, helping enterprises to improve their competitiveness and market share. Before selecting a 3PL provider, businesses must carefully evaluate their specific needs, the capabilities of the potential partner, and the compatibility of their business model.





