Electronic Waybills: The Advantages of Digital Transformation
Traditional paper air waybills (AWBs) are gradually being replaced by electronic air waybills (e-AWBs). According to IATA (International Air Transport Association), global e-AWB penetration will exceed 85% by 2023. However, many B2B companies and cross-border e-commerce sellers still lack understanding of this transformation.
Table of Contents
This article will provide a comprehensive analysis of the e-air waybill (e-AWB) as a digital solution to help B2B companies and e-commerce sellers understand how this technology can improve international logistics efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage.
What is e-AWB?
The electronic air waybill (e-AWB) is a digital version of the traditional air waybill (AWB) and has revolutionized the documentation process for international air cargo. Unlike traditional paper waybills, e-AWB uses an electronic data interchange (EDI) system to transmit shipment information between airlines, freight forwarders, ground handling providers, and customs, achieving a paperless process throughout the entire shipping process.
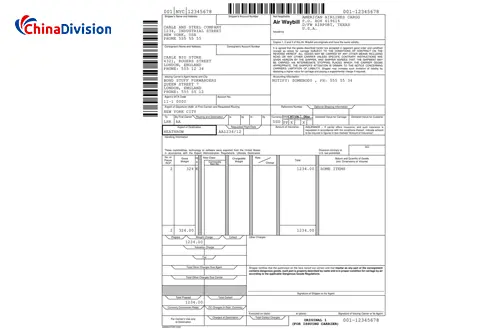
Its core features include:
Paperless: Eliminates physical processes such as printing, signing, and filing
Real-time: Data is synchronized across multiple systems, including airlines, customs, and freight forwarders
Standardized: Complies with IATA regulations e-AWB Specifications (e.g., MSG-016 Standard Format)
Pain Points of Traditional Paper Waybills
High Manual Entry Error Rate (Statistically, the error rate for paper documents reaches 12%)
Long Cross-Organization Transfer Time (On average, 48 hours are required for receipt confirmation)
High Storage Costs (Annual Storage Cost for a Single Paper Waybill is approximately $2.50)
Key Differences Between e-AWBs and Traditional Paper Waybills
Format: Traditional AWBs are paper documents, typically produced in multiple copies; e-AWBs are purely electronic records
Transmission Method: Paper AWBs require physical delivery; e-AWBs are shared in real time via an electronic system
Processing Speed: e-AWBs eliminate manual processing steps, significantly speeding up the process
Data Accuracy: Electronic transmission reduces the risk of human input errors
Cost Structure: e-AWBs save on the costs of printing, storing, and shipping paper documents
Why is the Logistics Industry Moving to Electronic Waybills?
Paper air waybills have long been the standard in the logistics industry. However, they are subject to issues such as human error, missing documents, and lengthy processing times. The e-AWB was introduced to address these pain points, offering the following features:
Fast processing speed—no need to prepare, print, or physically transport documents.
Reduces errors—Automation minimizes manual data entry errors.
Reduces costs—Reduced paperwork, printing, and administrative expenses.
Improves security—Digital records reduce the risk of document loss or tampering.
Environmental benefits—Reduces paper consumption and supports sustainability initiatives.
The core advantages of the e-AWB: Why embrace digitalization?
1. Significantly improves operational efficiency
The e-AWB eliminates the time-consuming printing, distribution, and archiving of paper documents. Traditionally, paper AWBs must be shipped with the shipment and manually verified at multiple points, a process that often results in processing delays of 12-24 hours. With the e-AWB, data is transmitted in real time, increasing cargo processing speed by over 30%.
2. Significantly reduces operating costs
The average processing cost of a paper AWB is approximately US$15-25 per shipment, while the e-AWB can reduce this cost to US$3-5 per shipment. For companies with an average monthly shipment volume of 1,000 shipments, annual savings could reach $150,000 to $250,000. Furthermore, e-AWB reduces document storage space and associated management costs.
3. Improved Data Accuracy and Consistency
Manual input errors are a common problem in traditional freight transport. e-AWB reduces the error rate to less than 1% through direct data transmission between systems. Standardized data standards also ensure that all relevant parties receive completely consistent information, avoiding customs clearance delays caused by discrepancies.
4. Enhanced End-to-End Visibility
When e-AWB is integrated with freight management systems, shippers can track shipment status in real time and obtain more accurate estimated times of arrival (ETAs). This transparency is particularly important for time-sensitive goods such as fresh produce and fashion items.
5. Simplified Compliance and Audit Processes
Electronic records are easier to store, retrieve, and audit, meeting increasingly stringent trade compliance requirements. All transaction histories are traceable, enabling rapid responses to regulatory inquiries.
6. Support for Sustainable Development Goals
e-AWB reduces paper consumption and the carbon emissions associated with shipping paper documents. IATA estimates that full adoption of e-AWB could reduce paper consumption by approximately 7,800 tons annually, equivalent to 187,000 trees.
- Improved Customer Experience
Fast processing, reduced error rates, and improved visibility enhance the end-customer delivery experience, which is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty and competitive advantage.
e-AWB FAQs
Is e-AWB suitable for small shipments?
Absolutely. In fact, small shipments stand to benefit more from the efficiency gains of e-AWB because fixed costs are more significantly spread.
Is e-AWB applicable to all types of cargo?
Yes, e-AWB is applicable to both general cargo and specialized cargo (including hazardous materials and temperature-controlled cargo). In fact, specialized cargo particularly benefits from the accuracy and efficiency of electronic processing.
Is e-AWB applicable to all countries?
While e-AWB is widely adopted globally, some countries (such as parts of the Middle East and Africa) still require paper copies for customs clearance. It is recommended to confirm the destination country's acceptance of electronic documents before shipping.
Is an e-AWB the same as a customs e-Declaration?
No. An e-AWB is a contract of carriage between a carrier and a freight forwarder, while an e-Customs Declaration is a declaration between a shipper and a customs officer.
Why choose Chinadivision's e-AWB solution?
At Chinadivision, we have seamlessly integrated the e-AWB process into our global network. This means that when you choose us as your international logistics and transportation provider, you benefit from:
Efficient document processing: Our system is designed to smoothly process e-waybill data, reducing paperwork and expediting the shipment process.
Faster customs clearance: Timely and accurate electronic submission of e-waybills information helps expedite customs procedures in various countries.
Real-time tracking and updates: Our online platform provides you with the latest information on your shipment based on the e-waybill data.
Reduced risk of delays and penalties: The accuracy and efficiency of e-waybill processing minimizes the possibility of errors that could lead to delays or penalties.
Sustainable Shipping Options: By choosing Chinadivision, you'll partner with a supplier committed to environmentally responsible practices through the adoption of electronic waybills.
Electronic waybills (e-AWBs) are more than just a trend; they're the future of international logistics and transportation. They eliminate the inefficiencies associated with paper waybills, enabling businesses to ship smarter, faster, and at lower costs.
Whether you're a large B2B company or a growing e-commerce seller, Chinadivision can tailor the most suitable e-AWB solution for you, helping you gain an efficiency advantage in the international market.





