The Difference Between Master Bill of Lading and House Bill of Lading
In international logistics and trade, the bill of lading is not only proof of the goods transportation contract, but also proof of ownership of the goods. Master Bill of Lading (MBL) and House Bill of Lading (HBL) are two common forms of bills of lading. They have significant differences in the issuing subject, function, purpose and legal status.
Table of Contents
- What is House Bill of Lading and when is it used?
- What is Master Bill of Lading and when to use it?
- What are the main differences between MBL and HBL?
- What are the benefits of House Bill of Lading?
- Can containers be tracked through House Bill of Lading?
- How does House Bill of Lading work?
- What are the main differences between Bill of Lading and House Bill of Lading?
- How to choose the right type of bill of lading?
- Move forward hand in hand with Chinadivision
Today, we will delve into the differences between Master Bill of Lading (MBL) and House Bill of Lading (HBL), as well as their practical application, to help you resolve any doubts you may have about freight forwarding bill of lading .
Many B2B companies often face this problem: the goods have been shipped, but the type of bill of lading is confusing. Should I choose MBL or HBL? What's the difference between them? These issues are not only related to the safe transportation of goods, but also directly affect the pickup of goods, transfer of cargo rights and possible dispute resolution.
What is House Bill of Lading and when is it used?
House Bill of Lading is a bill of lading issued by a freight forwarding company. It primarily serves shippers who wish to use a freight forwarder for LCL shipments. When a shipper's cargo is not large enough to fill a container, a freight forwarder will combine cargo from different shippers to form a full container for shipment. At this time, the freight forwarder will issue an HBL to each shipper as a certificate of property for their respective goods.
When to use HBL?
Small batch cargo: Applicable to less than container load (LCL), that is, goods from multiple shippers are assembled in one container.
Multi-stage transportation: When goods need to pass through multiple transportation methods (such as sea transportation, land transportation, air transportation), HBL can provide more detailed tracking information.
When shippers want to streamline the process and handle shipping through a freight forwarder.
Advantages of HBL:
Flexibility: Allows freight forwarders to adjust shipping plans based on customer needs.
Detailed Information: Provides more detailed cargo information to aid customs clearance and delivery.
What is Master Bill of Lading and when to use it?
Master Bill of Lading is a bill of lading issued directly by the shipping company to the shipper. It represents the shipowner's responsibility for the receipt and custody of the goods and is one of the core documents in maritime cargo transportation. MBL directly reflects the transportation contract relationship between the carrier and the shipper. It is a certificate of property rights and can be used directly to pick up the goods.
When to use MBL?
Full Container Cargo: Applicable to Full Container Cargo (FCL), that is, one shipper's cargo occupies one container.
Single mode of transportation: MBL can streamline the shipping process when goods travel through a single mode of transportation, such as ocean freight.
When the shipper wishes to establish a transportation contract relationship directly with the shipping company.
Advantages of MBL:
Authoritative: Issued by the carrier, it has higher legal effect.
Simplified process: suitable for simple transportation needs and reducing intermediate links.
What are the main differences between MBL and HBL?
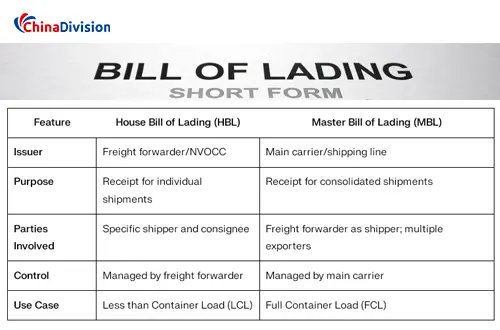
Issuing subject
MBL is issued by shipping companies, while HBL is issued by freight forwarders.
Legal status and scope of liability
MBL has the function of a property title document, which clarifies the rights and obligations between the shipping company and the final shipper or consignee. It is a formal transportation contract document. HBL is mainly applicable to the relationship between freight forwarders and their customers. Legally, it is not a document of property rights, but it can be used as proof of a transportation contract.
Usage scenarios
MBL is suitable for full container (FCL) transportation, while HBL is often used for less than container load (LCL) transportation, when the freight forwarder collects the goods of multiple customers and loads them into one container.
Bill of lading information content
MBL usually does not list the actual consignor or consignee information in detail, while HBL will list the final consignee, consignor and other information in detail.
Transferability
If the MBL is an instruction bill of lading, it can be transferred to a third party by endorsement, while the HBL is generally not transferable unless it is specifically stated to be transferable.
What are the benefits of House Bill of Lading?
Flexibility: Freight forwarders can customize HBL based on shipper needs to provide more flexible services.
Simplify the process: With a freight forwarder, shippers enjoy one-stop service and reduce the cost of communicating with multiple suppliers.
Cost-Effectiveness: LCL shipping is generally less expensive than FCL shipping and is especially suitable for shipping small quantities of goods.
Can containers be tracked through House Bill of Lading?
While HBL itself does not directly provide container tracking information, freight forwarders often use their internal systems or interfaces with shipping lines to track cargo status and provide real-time updates to shippers. So while HBL itself is not a tracking tool, the freight forwarder’s services ensure that shippers are kept up-to-date on their shipments.
How does House Bill of Lading work?
HBL works based on an agreement between the freight forwarder and the shipper. The freight forwarder acts as an intermediary, receives the shipper's goods, issues an HBL as a certificate of property, and then combines the goods into full containers and delivers them to the shipping company. The shipping company then issues an MBL to the freight forwarder, but the shipper information on the MBL is for the freight forwarder. HBL records the detailed information of the goods, including shipper, consignee, goods description, transportation route, etc. When the goods arrive at the destination, the freight forwarder picks up the full container of goods from the shipping company based on the MBL, and then distributes the goods to various shippers based on the HBL.
What are the main differences between Bill of Lading and House Bill of Lading?
Issuing party: B/L (bill of lading in a broad sense) can be issued by a shipping company or a freight forwarder, while HBL specifically refers to a bill of lading issued by a freight forwarder.
Property Certificate: Although both B/L and HBL are property rights documents, the property rights of HBL are usually governed by the agreement between the freight forwarder and the shipper.
Usage scenarios: B/L is suitable for various transportation scenarios, while HBL is more common in LCL transportation and transportation through freight forwarders.
Conversion of MBL to HBL: In some cases, shippers may need to convert HBL to MBL in order to connect directly with shipping lines or to meet specific country import requirements. This usually involves additional cost and time.
Risks of HBL: Although HBL provides flexibility, there are also risks, such as freight forwarder credibility issues, legal applicability, etc. Therefore, choosing a reliable freight forwarder is crucial.
Digital trends: With the digital transformation of the logistics industry, more and more freight forwarders are beginning to provide electronic HBL services to improve efficiency and transparency.
How to choose the right type of bill of lading?
As a professional third-party fulfillment service provider, Chinadivision recommends that enterprises choose the appropriate bill of lading type based on the following factors:
Cargo type: Choose MBL for full container goods and HBL for LCL goods.
Transportation method: Choose MBL for single transportation, and HBL for multi-section transportation.
Information needs: If you need detailed information, choose HBL, if you need simple transportation, choose MBL.
By rationally selecting the type of bill of lading, companies can improve logistics efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure the safety and traceability of goods. If you have more questions about MBL and HBL, welcome to contact Chinadivision, we will provide you with professional logistics solutions.
Move forward hand in hand with Chinadivision
As a professional third-party fulfillment service provider, Chinadivision is well aware of the importance of ocean bills of lading in logistics and transportation. We provide comprehensive freight forwarding services, including HBL and MBL issuance, cargo tracking, customs clearance assistance, etc. We provide one-stop services including cargo classification, packaging, transportation and customs clearance to help companies reduce logistics costs and improve efficiency.
Whether you are facing the challenge of LCL shipping or want to connect directly with the shipping company, Chinadivision can provide you with a one-stop solution. Our goal is to ensure your cargo reaches its destination safely and efficiently while reducing transportation costs and risks. For further assistance or questions about optimizing your shipping process, contact Chinadivision today!





