Cash on Delivery: a New Payment Option for Logistics Packages
Cash on Delivery (COD) is a flexible and convenient payment method that is popular in certain market environments. However, more than 68% of B2B companies are still experiencing a tearing growth between high order volume and low profit margins.
Table of Contents
- What is Cash on Delivery (COD)?
- How does cash on delivery (COD) work?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cash on Delivery (COD)
- Essential Analysis of COD and Cash on Demand
- Comparison between COD and Cash in Advance
- Common hot topics and answers
- Chinadivision's solution for international fulfillment service providers
- Is cash on delivery the right choice for your business?
This article will explore the comparison between COD and Cash in Advance based on the operating mechanism, advantages and disadvantages of COD, and combine the professional perspective of Chinadivision, an international fulfillment service provider, to provide feasible solutions for B2B companies or e-commerce sellers.
What is Cash on Delivery (COD)?
Cash on Delivery (COD) is also called "cash on delivery" or "pay on demand". It is a payment method where the buyer pays when the goods are received, rather than in advance. This method is popular in both B2C and B2B sales, especially in markets where credit card usage is limited or customers want to see the goods before paying. Essentially, the seller ships the goods first, and the customer settles the bill with cash, check or sometimes digital payment methods after receiving the goods.
How does cash on delivery (COD) work?
COD is a payment method that allows customers to pay for goods only when they receive them. This payment method is not only applicable to e-commerce, but also widely used in local delivery and international logistics. Its core is "one hand over the money, the other hand over the goods". The operation process of COD usually includes the following steps:
Customer order
Customers choose COD as a payment method when placing an order on the website or through other channels.
Shipping and invoicing
The seller ships the goods and attaches an invoice or payment receipt.
Logistics distribution
The logistics partner is responsible for delivering the goods to the customer and collecting the payment.
Collection and settlement
The logistics partner transfers the payment to the seller after deducting the handling fee.
It is worth noting that COD payment methods are not limited to cash. Customers can also choose to complete payment by check, bank card or even mobile payment tools.
When the buyer places an order, the seller delivers the goods to the buyer's designated delivery address through logistics channels. When the goods are delivered, the buyer needs to pay the delivery person to complete the transaction. This process seems simple, but it requires an efficient logistics network and a reliable payment processing mechanism to support it.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cash on Delivery (COD)
Advantages of COD
Enhance customer trust: COD allows customers to personally check the goods after receiving them and pay after confirming that the goods are correct. This payment method is especially suitable for customers who are not very confident about online shopping, and can effectively enhance customers' trust in the brand. The repurchase rate of COD sellers among Middle Eastern consumers has increased by 58%.
Reduce the risk of refunds: Since customers pay only after receiving the goods, sellers can reduce the risk of refunds caused by product quality problems.
Expand the customer base: COD provides a convenient payment method for customers who do not have credit cards or bank accounts, thereby expanding the potential customer base.
Reduce the risk of fraud: Compared with online payment, COD can reduce the losses faced by sellers due to credit card fraud or electronic payment disputes.
Promote sales growth: For products with higher prices or requiring on-site inspection, the COD model can lower the purchase threshold for buyers and promote sales growth.
Disadvantages of COD
Increased return risk: Customers may refuse to pay and return the goods after receiving them because they are not satisfied. This not only increases the cost of returns, but may also lead to inventory backlogs.
Cash flow pressure: Sellers need to wait for customers to pay after the goods are shipped. The average 45-day collection cycle consumes 12-18% of operating funds, which may put some pressure on cash flow.
Increased logistics costs: COD usually requires logistics partners to provide additional services (such as collecting payment on behalf of the goods), which may increase logistics costs.
Operational complexity: COD requires sellers to work closely with logistics partners to ensure timely recovery and processing of payments.
Essential Analysis of COD and Cash on Demand
COD (Cash on Delivery) is a transaction mode that triggers payment with physical delivery, which is common in e-commerce and bulk logistics scenarios
Cash on Demand (Payment on Request) is an instant payment requirement based on a credit certificate, which is mostly used in the field of B2B trade financing
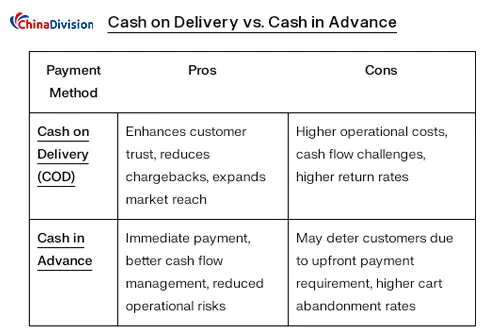
Comparison between COD and Cash in Advance
The common comparison method is Cash on Delivery (COD) and Cash in Advance (CIA), that is, the buyer prepays the goods before the order is shipped. Both methods have their own advantages, but also their own pros and cons.
Cash on Delivery (COD)
Payment time: payment when the goods are delivered.
Risk sharing: buyers bear certain risks, and sellers bear logistics and collection risks.
Consumer confidence: improve consumer purchasing confidence and reduce concerns about online payments.
Cash in Advance (CIA)
Payment time: payment when placing an order.
Risk sharing: buyers bear all risks, and sellers have no collection and logistics risks.
Cash flow: sellers receive payment in a timely manner, reducing cash flow pressure.
COD and prepayment are two very different payment methods. Prepayment requires customers to pay for goods before the goods are shipped. This method is less risky for sellers, but may make customers feel unsafe. In contrast, although COD is more risky for sellers, it is more customer-friendly and can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Common hot topics and answers
Is the COD model applicable to all goods?
The COD model is applicable to most goods, but some special goods (such as fragile goods, dangerous goods, etc.) may not be suitable for the COD model. In addition, for goods that are too expensive or require professional installation, sellers may need to consider other payment methods to reduce the risk of returns.
How to reduce the return rate in COD transactions?
Reducing the return rate in COD transactions requires multiple aspects. First, sellers should provide accurate product descriptions and clear picture displays to reduce the number of buyers returning goods due to inconsistent product descriptions. Second, sellers should establish a complete after-sales service system to handle buyers' complaints and return requests in a timely manner. Finally, by cooperating with logistics companies to provide flexible delivery time and appointment delivery services, the return rate caused by no one signing can also be reduced.
What is the prospect of the COD model in international B2B transactions?
With the rapid development of cross-border e-commerce and the continuous improvement of consumers' requirements for shopping experience, the COD model has broad prospects in international B2B transactions. Especially in those areas where the online payment system is not well developed or consumers do not trust online payment, the COD model will become an important force to promote the growth of e-commerce transactions. At the same time, with the continuous improvement of cross-border logistics networks and the continuous advancement of payment processing technology, the application of the COD model in international B2B transactions will be more extensive and convenient.
How to choose a payment method that suits you?
Whether to choose COD or prepayment depends on your business model and risk tolerance. If you want to improve customer trust and expand your customer base, COD may be a good choice. However, if you are more concerned about cash flow and risk control, prepayment may be more suitable for you.
Chinadivision's solution for international fulfillment service providers
In response to the challenges and problems of the COD model in B2B e-commerce transactions, Chinadivision has a complete cross-border logistics network that can ensure that goods are delivered to buyers quickly and accurately. At the same time, we have established partnerships with many well-known logistics companies to provide buyers with a variety of logistics options.
Is cash on delivery the right choice for your business?
Whether to offer cash on delivery (COD) as a payment method depends on your business model, target market, and ability to manage related risks. Although cash on delivery can provide a valuable option for customers who prefer cash on delivery, it also brings challenges such as payment delays, processing risks, and the possibility of returns.
Through the explanation and analysis of this article, I believe you have a deeper understanding of the application of the COD model in B2B e-commerce transactions. If you encounter any problems or need professional solutions during COD transactions, please feel free to contact Chinadivision's international fulfillment service providers. We will wholeheartedly provide you with efficient, safe and professional service support.





